Describe the Internal Structure of Monocot Root
These cells may store food reserves. Root hairs are always single celled.
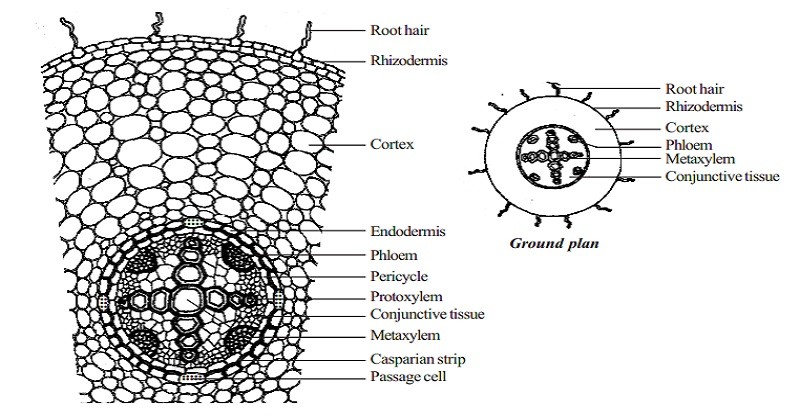
Compare The Anatomical Structure Of A Dicot Root With A Monocot Root
In dicot roots the vascular structures are located in the middle of the root surrounded by vascular cambium.

. Primary Structure of Monocot Root Anatomy Monocot roots shows following distinct regions. It contains water proof casparian strips that control water flow into the vascular tissue. Monocot roots have a larger number of vascular structures than dicot roots.
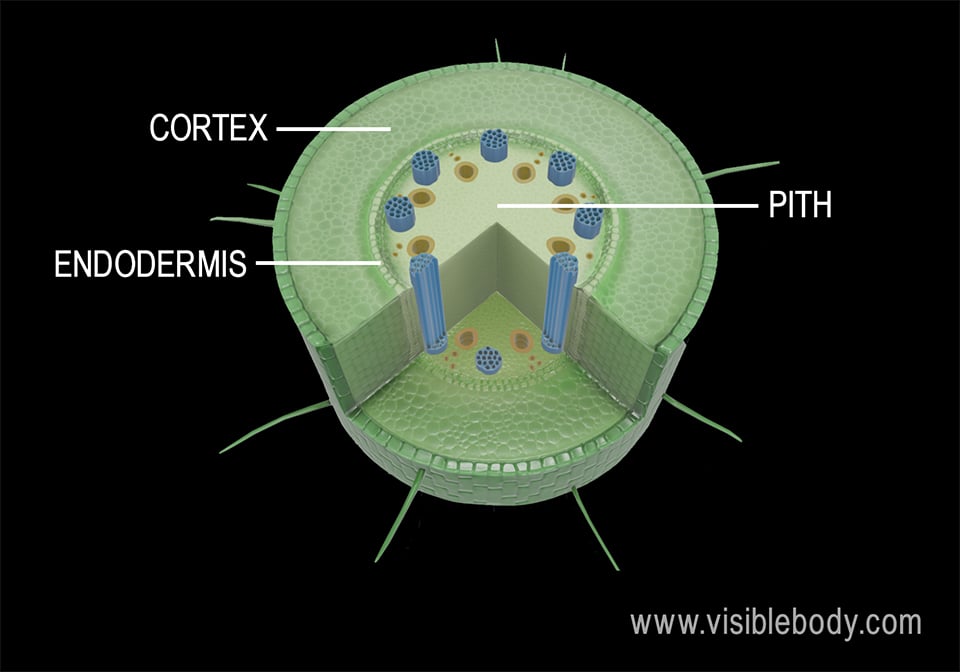
It lies just below the epidermis. 2 Pith is well developed in monocotyledon root. Describe the structure of the root and state the function of its components - internal and external structures to include drawings of transverse and longitudinal sections through a young dicotyledon root to show the following components.
Identifying characteristics of the internal structure of monocot root. The internal structure of a typical monocotyledon root is similar to dicotyledon root. Internal structure of monocot root The epidermis on the outside of the root consists of a single layer of cells.
Unicellular root hairs are present. The vessels of xylem are rounded or oval shape. The radial and the inner tangential walls of endodermal cells are thickened with suberin.
Root hairs are always single celled. Rhizodermis or epiblema It is the outermost layer of the root. The cortex forms the layer below the epidermis and is made up of thin-walled parenchyma cells.
It lies below the epidermis. Internal study is equally importantÃÂ In medical entrance examination you will surely get a question from internal study of different parts of plant and of animal as well. Epiblema is the outermost single layer made from compactly arranged parenchymatous cells without intercellular space.
Monocot stems have the majority of their vascular bundles near the exterior border of the stem. Rhizodermis or epiblema The outermost layer of parenchymatous cells without intercellular spaces. It contains more cuticle than dicot roots.
It consists of a single row of thin-walled parenchymatous cells without any intercellular space. Epidermis of root is also called epiblema or piliferous layer pilus hair. This is the structure of the primary root of the monocot plants.
Structurally monocot dicot stems are quite different. I The circular stem may have depressed structures due to the presence of lateral branches. 1 Number of xylem bundles are more than six Polyarch in monocotyledon root exceptionally the number of xylem bundles are two to six in onion.
Describe the difference between monocotyledon and dicotyledon roots. Anatomical structure of Monocot Stem. Internal Structure of Monocot Root Biology definition Anatomy of primary monocot root 1.
Many epidermal cells prolong to form long hairy bodies the typical unicellular hairs of roots. It is also known as Rhizodermis or Piliferous layer. Here we are going to take a look to internal structure of stem roots leaves.
Internal Structure of Orchid Root. Xylem and phloem are presents numerous in number in a monocot root. In this study focus on identifications of the internal structure of monocot stem.
In monocot roots xylem and phloem tissue bundles are arranged in a circular fashion around the central pith which consists of ground tissue parenchyma. The internal structure of the monocot roots shows the following tissue systems from the periphery to the centre. It is the single outermost layer composed of small thin-walled somewhat barrel-shaped parenchymatous cells.
It is the outermost layer. Pith Features of Different Regions of Monocot Root 1. They are epiblema or rhizodermis cortex and stele.
Internal Structure of Dicot Root Bean A thin transverse section of dicot root shows the following structures. It has single layered epidermis and epidermal hairs are absent. Epiblema is single covered thin-walled colorless polygonal without intercellular spaces with the existence of unicellular root hairs.
Stomata and cuticle are absent. Stemis so responsible inside. I Unicellular root hairs are present in the epiblema in which cuticle is absent.
This structure lies between the vascular bundle and helps in storage of water. The main difference of monocot stem from dicot stem is that here in monocots the ground tissue is NOT differentiated into. Internal Structure of Monocot Stem Transverse Section TS The anatomy or internal structure of a monocot stem can be studied by a Transverse Section TS taken through the internode of a monocot plant such as grass bamboo maize Asparagus etc.
It is made up of single layer of barrel shaped parenchymatous cells. The outer walls of epidermal cells are not cutinised. Some of the epidermal cells have root hairs.
An extension of specialized root epidermal cells increasing surface area for absorption of water minerals. Outer layer of cells skin. It comprises of 2-3 layers of thick-walled.
Cortex consists of oval or rounded loosely arranged parenchymatous cells. Whats more it has fibrous roots. Region between epidermis vascular cylinder.
Monocot Root has xylem and phloem within an alternating manner. Cuticle and stomata are absent. Supports plant parts stores food.
It is single-layered and composed of thin- walled cells. Internal Structure of Monocotyledon Root. Conjunctive tissue at a monocot root is mostly sclerenchymatous at times it could be parenchymatous also.

Identifying Characteristics Of The Internal Structure Of Dicot Root Qs Study
Explain The Primary Structure Of Monocot Root Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Primary Structure Dicotyledonous Monocotyledonous Root Leaf Plantlet

Preparation And Study Of T S Of Dicot And Monocot Roots And Stems Primary

Detailed Structure Of A Portion Of Dicot Root Biology Plants Plant Science Study Biology
Identifying Characteristics Of The Internal Structure Of Dicot Root Qs Study
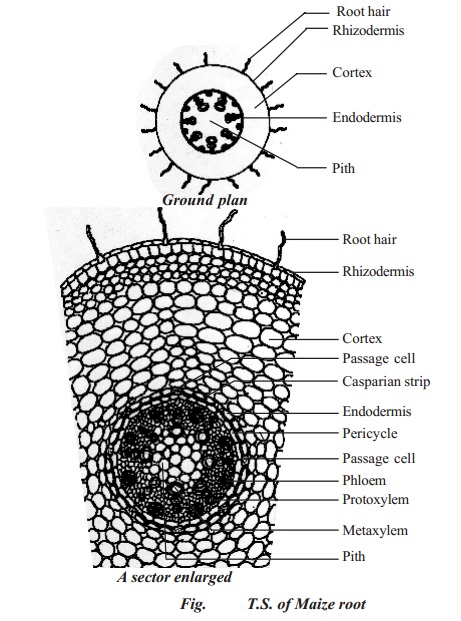
Primary Structure Of Monocotyledonous Root Maize Root

Identifying Characteristics Of Internal Structure Of Monocot Root Qs Study
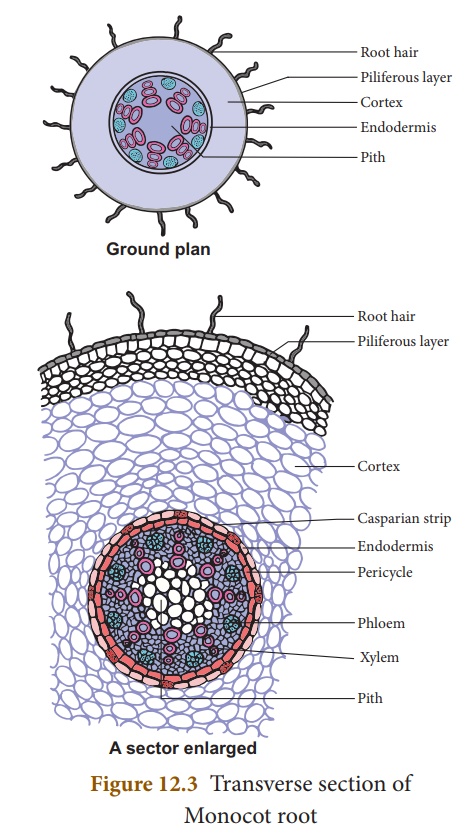
Internal Structure Of Monocot Root Maize
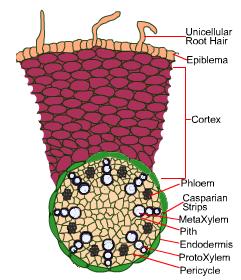
Monocot Root A Complete Anatomy With Diagram
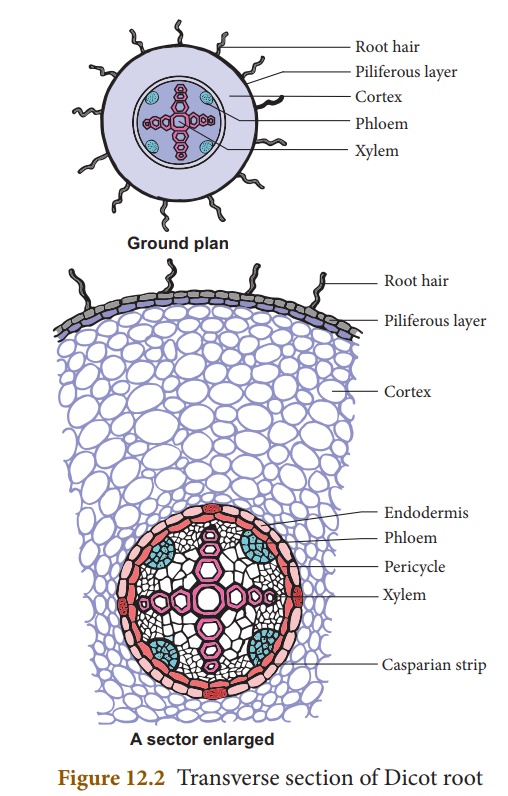
Internal Structure Of Dicot Root Bean
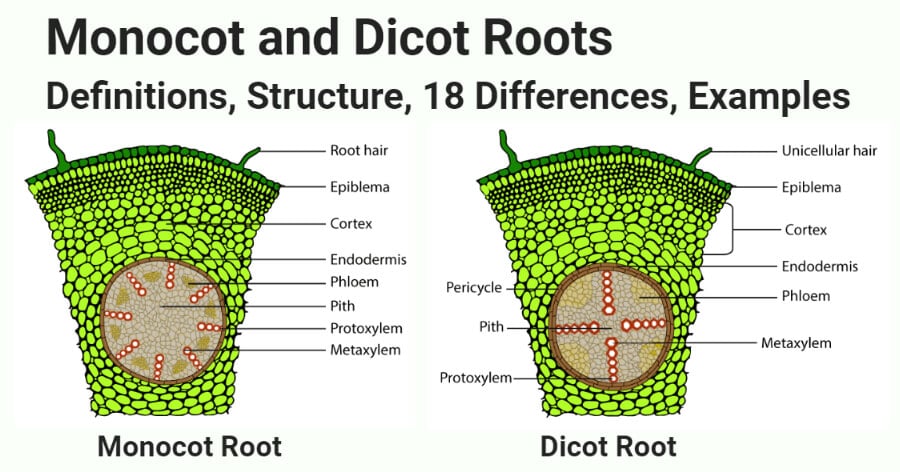
Monocot Vs Dicot Roots Definition Structure 18 Differences Examples

Solution Anatomy Of Monocot Root Studypool
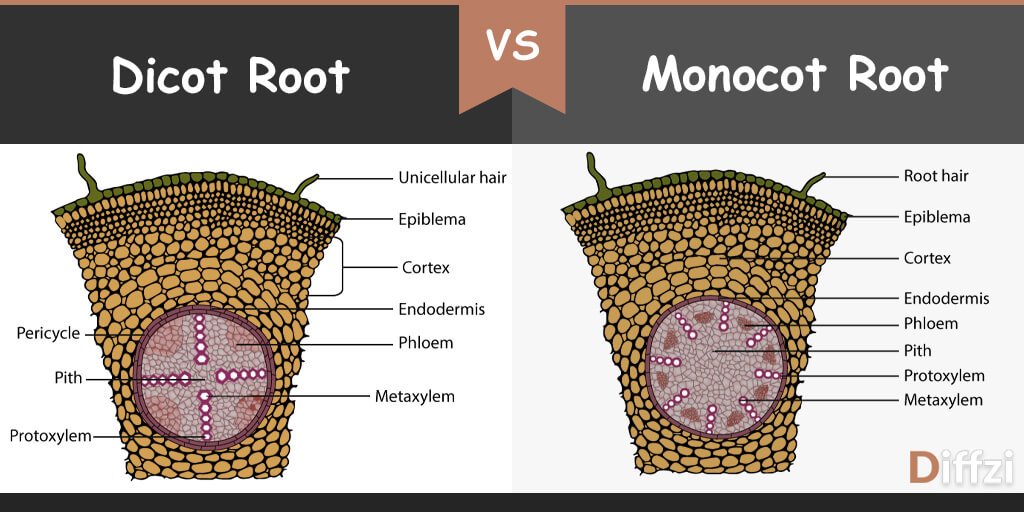
Dicot Root Vs Monocot Root Diffzi

Explain The Internal Structure Of Dicot Root With Help Of Well Labelled Diagram And Also Differentiate Brainly In
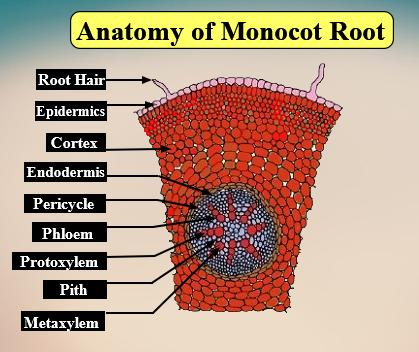
Discuss The Internal Structure Of Monocot Roots Class 11 Biology Cbse

Internal Structure Of Monocot Root Definition Examples Diagrams
Explain The Internal Structure Of Dicot Root With The Help Of Well Labelled Diagram And Also Differentiate Between Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Comments
Post a Comment